Comprehending Wastewater Therapy Processes and Their Environmental Influence
The details of wastewater therapy procedures play a pivotal role in mitigating ecological difficulties linked with water air pollution. Each stage, from preliminary to sophisticated therapies, is created to resolve specific impurities, inevitably securing both public health and marine communities.
Summary of Wastewater Treatment
How is wastewater changed right into a safe resource for the setting? Wastewater treatment is a vital process designed to get rid of pollutants from used water, therefore guarding public health and wellness and protecting ecosystems. This procedure begins with the collection of wastewater from household, commercial, and commercial resources, which is then routed to treatment centers.
At these centers, various physical, chemical, and organic techniques are used to treat the wastewater. First screening gets rid of big debris, complied with by sedimentation to separate much heavier solids. Subsequently, organic therapies, such as triggered sludge procedures, use microbes to break down natural matter. These techniques not only minimize pollutant degrees but additionally help with the recuperation of important nutrients.
The treated effluent can be securely discharged right into natural water bodies or recycled for watering and industrial functions, promoting resource preservation. Additionally, the treatment procedure generates biosolids, which can be repurposed as plant foods or dirt amendments, additionally boosting sustainability.
Stages of Treatment Processes
The wastewater treatment process commonly includes three main phases: initial, key, and secondary treatment. Each phase offers a distinctive role in decreasing the contaminant lots and guaranteeing the effluent satisfies ecological criteria before discharge.

The key treatment stage focuses on the physical splitting up of suspended solids from the wastewater. Via sedimentation, much heavier bits resolve at the base of sedimentation containers, developing sludge, while lighter materials, such as oils and oils, float to the surface area and are skimmed. This procedure dramatically lowers the natural and not natural tons in the wastewater.
Additional treatment is an organic process intended at additional reducing the focus of organic issue. This stage is essential for attaining the required biochemical oxygen need (BODY) decrease, eventually leading to cleaner effluent ready for discharge or additional treatment.
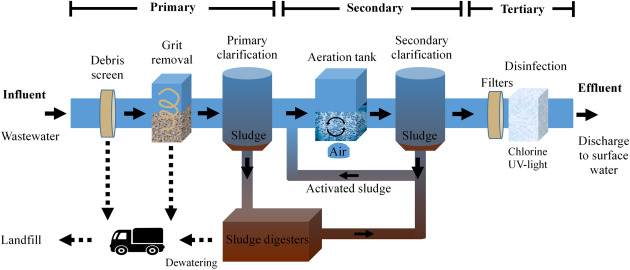
Advanced Treatment Technologies
Adhering to the additional therapy processes, progressed treatment modern technologies play an important duty in further boosting the quality of treated wastewater. These modern technologies are developed to get rid of residual pollutants that are not effectively gotten rid of throughout main and second treatments, making sure the effluent meets rigid regulatory requirements.
Amongst the widely used innovative treatment techniques are membrane look at this site layer filtration, reverse osmosis, and progressed oxidation processes. Membrane filtering, consisting of microfiltration and ultrafiltration, works in dividing great particles, microorganisms, and colloids from the water (Wastewater). Reverse osmosis makes use of semi-permeable membranes to remove liquified solids, causing premium water ideal for numerous applications
Advanced oxidation procedures (AOPs) employ strong oxidants to break down natural toxins, like this including pharmaceuticals and personal care products that are resistant to traditional therapy. These approaches enhance the biodegradability of complex compounds, facilitating their removal.
One more considerable innovation is making use of organic nutrient elimination procedures, which especially target nitrogen and phosphorus, preventing eutrophication in receiving water bodies. Overall, advanced treatment modern technologies are vital for accomplishing greater levels of filtration, promoting water reuse, and protecting public health and wellness while resolving the obstacles related to wastewater monitoring.
Environmental Benefits of Treatment
Various ecological benefits emerge from reliable wastewater therapy processes that add to ecosystem wellness and sustainability. Primarily, these processes significantly lower the launch of dangerous contaminants into all-natural water bodies, which assists preserve aquatic ecosystems. By getting rid of pollutants such as heavy steels, nutrients, and microorganisms, treated wastewater minimizes the danger of waterborne diseases and advertises biodiversity in marine environments.
In addition, wastewater therapy facilities usually utilize advanced modern technologies that allow water recycling and reuse. This practice not just conserves fresh water resources yet likewise reduces the need on natural water materials. Enhanced nutrient elimination from wastewater can also stop eutrophication, a process that brings about algal flowers and succeeding oxygen exhaustion in marine systems.
Furthermore, reliable treatment procedures can minimize greenhouse gas discharges, particularly methane and nitrous oxide, which are often released throughout neglected wastewater disintegration. By capturing and using biogas from anaerobic digesters, centers can convert waste right into renewable resource, consequently adding to a reduction in fossil gas dependence.
Challenges and Future Patterns
While the ecological benefits of wastewater treatment are clear, a number of obstacles Look At This persist that impede optimum outcomes in this field. One major concern is maturing infrastructure, which typically brings about inefficiencies and boosted functional prices - Wastewater. Many treatment plants were created decades earlier, and their capacities do not align with modern demands, that include more stringent governing criteria and greater quantities of wastewater due to urbanization

Looking ahead, there is an expanding focus on resource recovery and round economic climate principles within wastewater therapy. Advancements such as anaerobic digestion, which can produce biogas, and progressed filtration technologies are obtaining grip. These methods not just improve treatment effectiveness yet additionally advertise sustainability.
Ultimately, attending to these obstacles needs collaboration among stakeholders, investment in technology, and a dedication to ongoing study. By embracing these fads, the wastewater treatment field can develop to fulfill the demands of a transforming atmosphere and culture.
Conclusion
In final thought, wastewater treatment procedures play a crucial duty in boosting environmental quality and public health. The multi-stage treatment framework, coupled with sophisticated innovations, successfully minimizes air pollution and advertises lasting water monitoring.